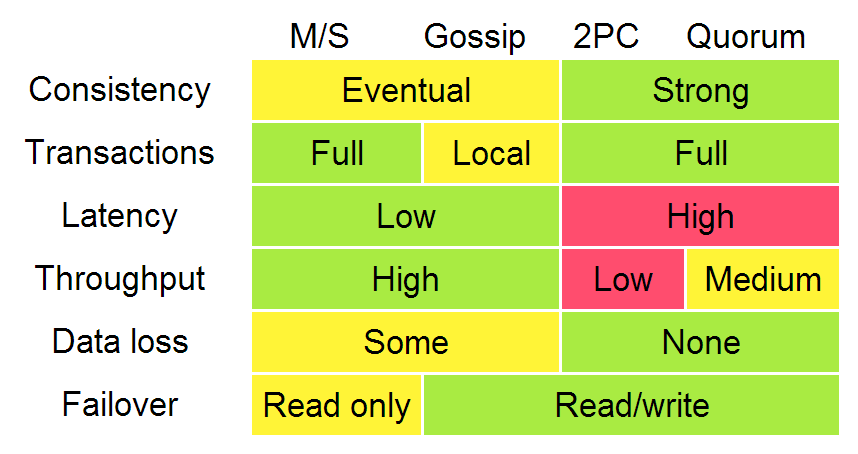
Replication
分类
Two basic replication approaches
- Synchronous replication
- Asynchronous replication
根据是否会产生分歧分为
- single copy systems
- 副本间保持一致性,只有一个副本是活跃的
- 常见算法
- 1n messages (asynchronous primary/backup)
- 2n messages (synchronous primary/backup)
- 4n messages (2-phase commit, Multi-Paxos)
- 6n messages (3-phase commit, Paxos with repeated leader election)
- multi-master systems
Primary/backup replication
- asynchronous primary/backup replication
- MySQL, MongoDB
- synchronous primary/backup replication
Two phase commit (2PC)
MySQL Cluster provides synchronous replication using 2PC
Partition tolerant consensus algorithms
- Paxox
- Raft
网络分区,Majority decisions ( (N/2 + 1)-of-N)
Roles
leader follower
Epochs
During each epoch only one node is the designated leader
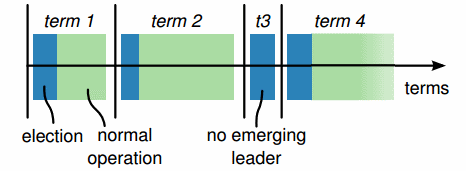
Leader changes via duels
所有节点开始都是follower,leader维护心跳,follower通过心跳检测leader的状态和是否发生分区。
当节点检测到leader出问题后,它切换到“candidata”状态,开始一轮选举,竞选leader。
为了成为leader,节点必须接受大多数的投票。简单的投票规则是先来先得。同时增加一个随机的等待时间来解决同时请求选举的问题。
Numbered proposals within an epoch
During each epoch, the leader proposes one value at a time to be voted upon. Within each epoch, each proposal is numbered with a unique strictly increasing number. The followers (voters / acceptors) accept the first proposal they receive for a particular proposal number.
Paxos Raft ZAB
Paxos 最有名的强一致性分区容忍算法,在Google的多个系统上使用。主要问题是Paxos只解决一轮一致性决策,实际的实现中往往需要多轮Paxos算法。
ZAB Zookeeper Atomic Broadcast protocol. 用在 Apache Zookeepr 里。
Raft 设计目标之一是易懂。Etcd项目使用该算法。
Replication methods with strong consistency
Primary/Backup
- Single, static master
- Replicated log, slaves are not involved in executing operations
- No bounds on replication delay
- Not partition tolerant
- Manual/ad-hoc failover, not fault tolerant, "hot backup"
2PC
- Unanimous vote: commit or abort
- Static master
- 2PC cannot survive simultaneous failure of the coordinator and a node -during a commit
- Not partition tolerant, tail latency sensitive
Paxos
- Majority vote
- Dynamic master
- Robust to n/2-1 simultaneous failures as part of protocol
- Less sensitive to tail latency
Weak consistency model protocols
Eventual consistency with probabilistic guarantees
Quorum
A quorum is the minimum number of votes that a distributed transaction has to obtain in order to be allowed to perform an operation in a distributed system. A quorum-based technique is implemented to enforce consistent operation in a distributed system.
Quorum-based voting in commit protocols
Quorum-based voting for replica control
State machine replication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/State_machine_replication
Amazon's Dynamo
set(key, value) get(key) Dynamo prioritizes availability over consistency;t does not guarantee single-copy consistency.Instead, replicas may diverge from each other when values are written; when a key is read, there is a read reconciliation phase that attempts to reconcile differences between replicas before returning the value back to the client.
[ Client ]
|
( Mapping keys to nodes )
|
V
[ Node A ]
| \
( Synchronous replication task: minimum durability )
| \
[ Node B] [ Node C ]
A
|
( Conflict detection; asynchronous replication task:
ensuring that partitioned / recovered nodes recover )
|
V
[ Node D]
Consistent hashing Partial quorums Conflict detection and read repair